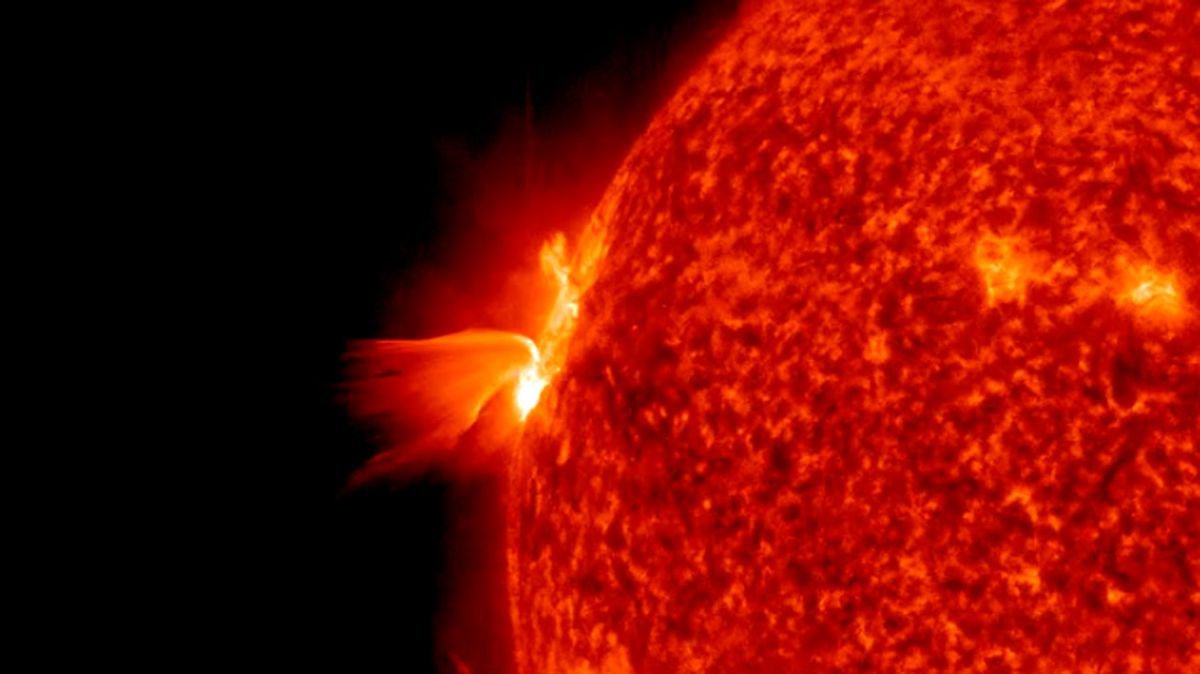
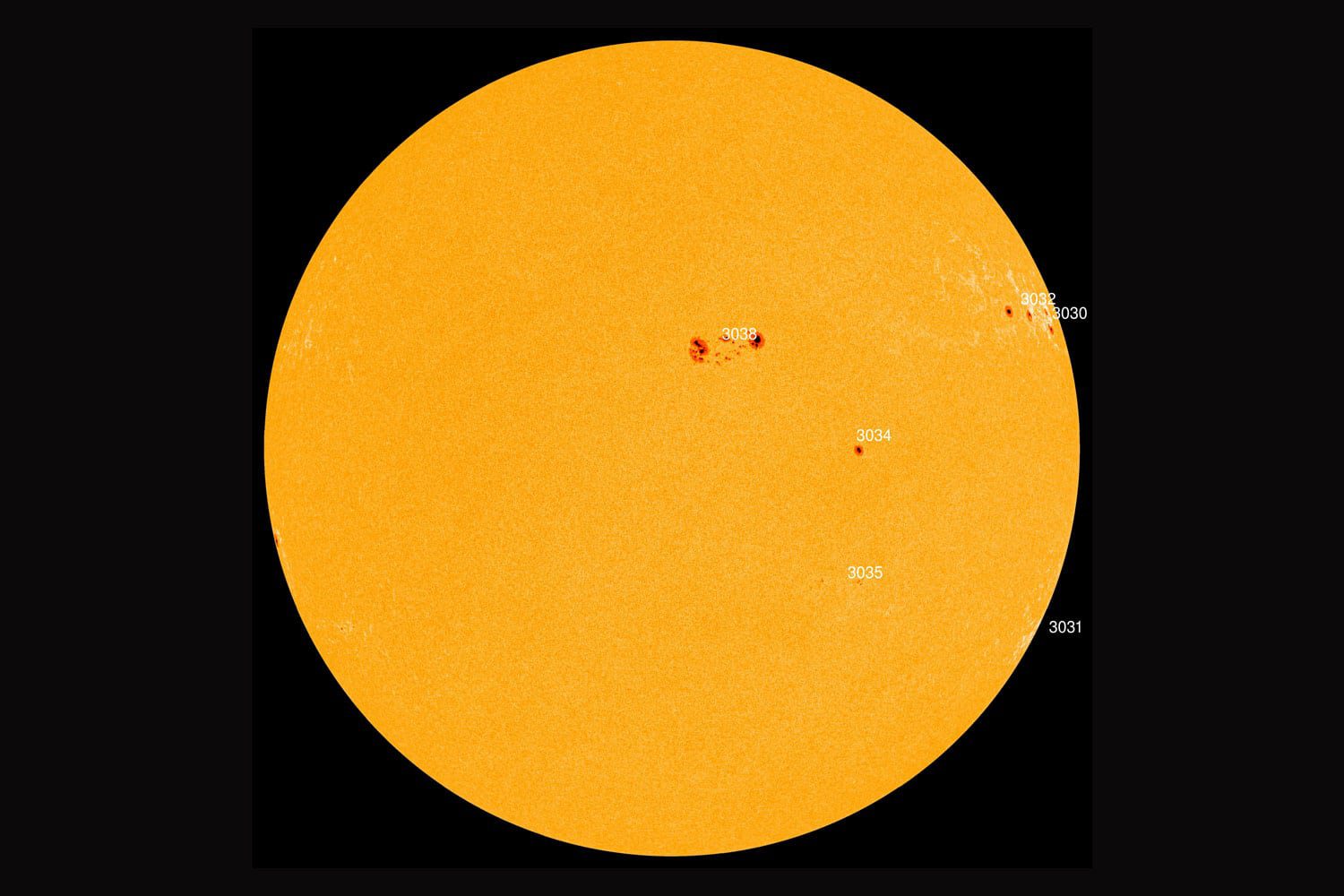
In just 24 hours, a sunspot pointing directly at Earth has doubled in size. Scientists fear this could lead to a geomagnetic storm.
Sunspots take their name from a color darker than the rest of the sun’s surface. On the other hand, its temperature is lower, while the magnetic field is stronger. Some of these structures are small, up to several kilometers in diameter. On the other hand, other species can grow for hundreds of thousands of kilometers. As for its duration, it ranges from several days to several months.
Read also: The comet burned like coal. This is how the sun dealt with it
Some sunspots even move across the surface of our star, shrinking or expanding during this time. In this case, the object known as AR3038 is of particular interest to scientists. The spot targets the Earth directly, contains an unstable magnetic field, and in just 24 hours has doubled in size.
Given the ability of sunspots to generate solar flares, it’s impossible not to think about the potential consequences of an AR3038 eruption. The intense blast of radiation caused by the release of magnetic energy from sunspots can have a noticeable effect on our planet. Eruptions can occur multiple times, the best evidence for this being the fact that one spot in March caused at least 17 eruptions.
AR3038 sunspot doubled in size in 24 hours
To divide the flares into several groups, scientists propose classes such as A, B, C, M and X. Each subsequent one is ten times more powerful than the previous one, and AR3038 sunspot can lead to a Class M glow. People on Earth, but astronauts in space External may encounter some problems. These can also apply to wireless communications on the surface.
Apart from these unpleasant consequences, it is also worth paying attention to slightly different consequences. It is, of course, the phenomenon of the aurora borealis, i.e. a colorful light show, that usually occurs near the poles. The stronger the glow, the closer the aurora is to the equator. There is a good chance that it will appear soon at slightly lower latitudes than usual.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.