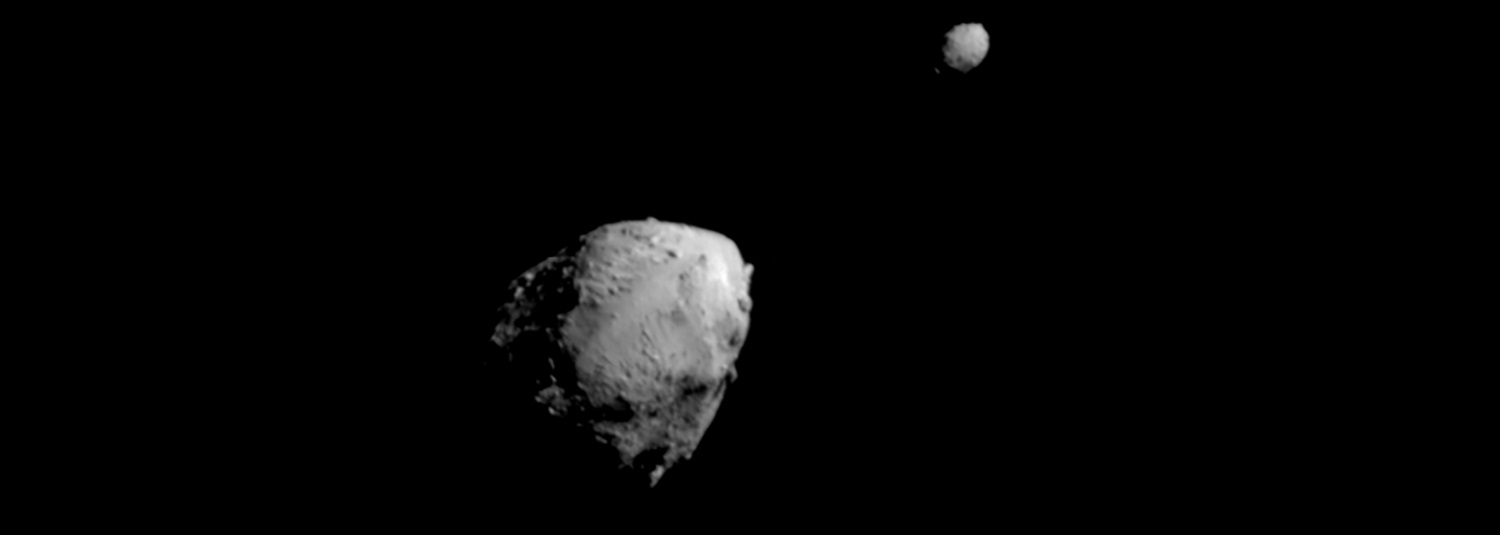
At least that’s the case with the object known as Didymos, made famous thanks to the DART mission. As part of that, the probe deliberately crashed into the surface of the asteroid’s moon, Dimorphosa. On the other hand, Didymus is a slightly larger body, with a diameter of about 390 meters.
Read also: This is how Dimorphos was created – the target of the DART mission, which may determine the fate of the Earth
Recently, astronomers have been interested in how an asteroid might behave. They noticed that due to the increased speed of rotation, stones were being thrown into space. What values are we talking about? It is estimated that Didymus only needs two hours and sixteen minutes to make a full revolution.
The results so far on this matter have been presented in the form of a raw version available in the website’s database arXiv. As the post’s authors note, the effects of such a rapid rotation are most strongly felt at the equator of the tested object. In this region, rocks and dust can be expelled from the surface, and end up in space. Over time, they fall again, starting the next cycle of rotation of matter inside the asteroid. Of course, some of these could be lost or fell on Dimorphosa’s natural satellite.
A slightly smaller object, Dimorphos, orbits the asteroid Didymus
The DART mission was not the first attempt to explore the system that consists of an asteroid and its moon. It was previously explored by the European Space Agency’s HERA mission. Particle dynamics studies then relied on the available shape model, known physical parameters and orbital information about Didymos and Dimorphos.
Thanks to DART (Double asteroid reorientation test) It was possible to prove that it is possible to change the flight path of a potentially threatening object. The results were all the more impressive because the “rocket” wasn’t particularly huge, and preparations for the entire project were far from perfect. Despite this, the scientists responsible for this mission have claimed success. Not only did Dimorphos’ orbital path change dramatically – the moon itself didn’t break into pieces, which was just as important.
Read also: The Chinese will collect samples from a passing asteroid. They have already chosen a specific goal
So if one day an asteroid similar to the one that wiped out the dinosaurs 66 million years ago turns out to be heading towards our planet, humanity may not be automatically written off. Of course, in terms of size, Dimorphos is hard to compare to the object that created the Chicxulub crater, but in the future, it’s likely engineers will also look at candidates slightly larger than Dimorphos. However, these may only be attempts, not actual actions within Planetary Defense.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.