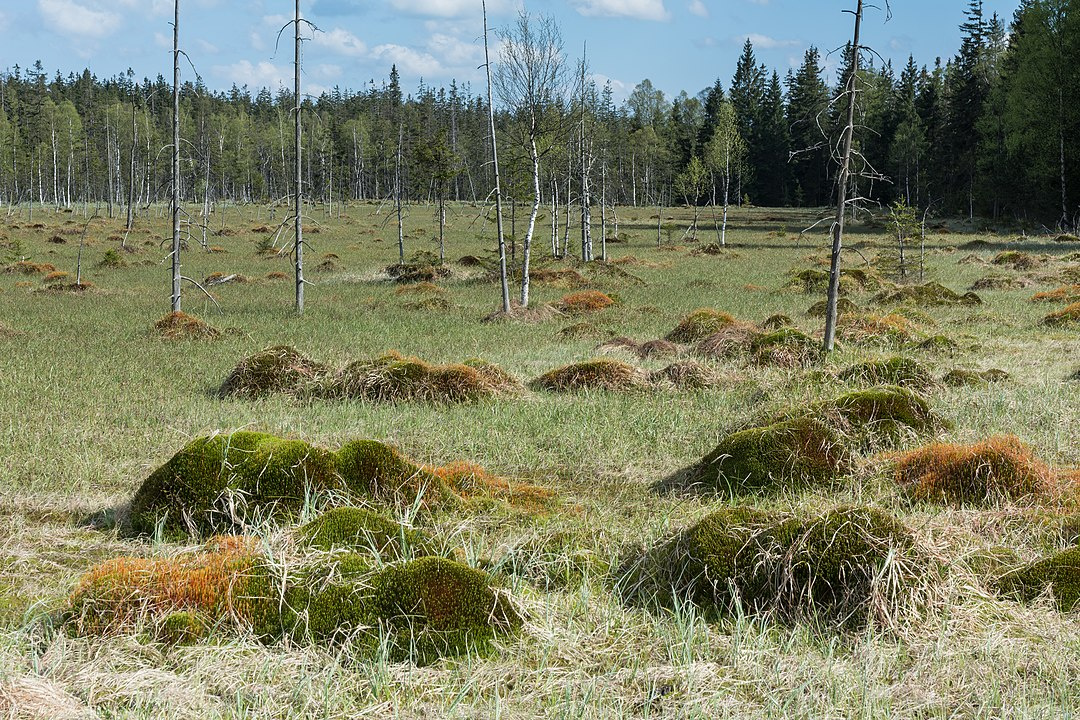
Some regions of our planet cover only 1% of its surface, while storing more than 20% of circulating carbon dioxide.
Because of this high efficiency, it seems that it is necessary to protect these places. These include swamps that people intentionally drain and then use for farming. In addition, the negative impact of deforestation, which also contributes to the drying of wetlands with salt and fresh water, should not be forgotten.
New results have been presented in this regard on the pages Science. The post’s authors say it’s not too late to reverse negative trends and prevent wetlands from disappearing completely. In their opinion, the key to success will be the use of the so-called resaturation, that is, the process of returning the natural environment to its original state, before the damage caused by human activity.
It’s never too late to work
“Each year, about 1 percent of the world’s wetlands disappear due to pollution or swamp drainage for agriculture, development and other human activities. Once a disturbance occurs, wetlands release massive amounts of carbon dioxide from the soil, which is equivalent to about 5 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions annually.They are exposed to the air for hundreds or even thousands of years and begin to decompose rapidly, releasing greenhouse gases, resulting in an invisible CO2 cascade flowing into the atmosphere.. Brian R. Silliman of Duke University explains
The high efficiency of wetlands is related to the fact that they consist of plants close to each other. Compact root systems above ground retain the density and elements of their structure, while protecting the soil from erosion or drying out. As a result, plants develop more efficiently and can retain much more carbon dioxide. With the ability to restore these ecosystems, scientists will be able to re-make them capable of absorbing one of the most important greenhouse gases.
In the case of peatlands, the plants that make up them act like sponges, absorbing huge amounts of water. This not only facilitates growth, but also helps keep dead algae deep beneath the surface. As a result, peat up to 10 meters thick does not dry out and leaches and releases stored carbon into the atmosphere. Over time, the amount of algae increases as well as the amount of carbon hidden beneath the surface.
Efficiency record for carbon dioxide absorption
The authors of the new research seek to carry out the process of re-normalization, which will enable the reconstruction of damaged wetlands or peat bogs. Scientists have also calculated that the oceans and forests contain the most carbon dioxide on a global scale. Immediately behind them are wetlands, which occupy a much smaller area. Taking into account the amount of carbon dioxide stored per square meter, it turns out that wetlands store about five times more than forests and up to 500 times more than oceans.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.