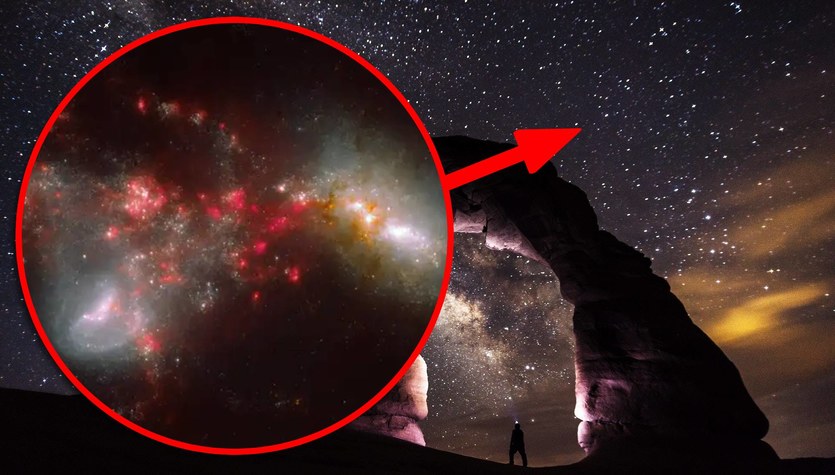
over here The image shows the collision of galaxies IC 1623 and the constellation Pisces. The event is located at a distance About 275 million light-years from the sun. His research is conducted by his manager’s team Lee Armos of the California Institute of Technology.
The team benefited from James Webb Space Telescope To take a closer look at four relatively bright nearby galaxy mergers to determine how they work.
The merger causes drastic changes in the shape and content of the galaxy (…) so we really need to understand the process to see how galaxies evolve. – He said Vivian Yu of the University of California, IrvineHe is a member of the research team.
Scientists noticed this during the collision of both galaxies Huge streams of matter are releasedAs well as shock waves that cross both galaxies.
these The processes are especially intense in the red spots shown in the pictureThey are star forming regions. They probably were concentrated due to the effect of shock waves.
Expectancy turns out to be an equally interesting aspect of this collision Increasing activity of supermassive black holeswithin both galaxies.
Scientists believe that during such an event their activity It should rise significantly. it’s because of Then supermassive black holes devour the matter around themWhile emitting huge amounts of radiation. At the moment, however, such a phenomenon has not been observed in IC 1623 crash.
This may indicate that this activity simply does not exist or that black holes are too hidden Inside the collision of galaxiesThey have not yet done the expected mechanism.

“Prone to fits of apathy. Introvert. Award-winning internet evangelist. Extreme beer expert.”