Our partner's advertising links are included in the text.
XRISM is a mission prepared by NASA and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and its main goal is Analysis of X-rays emitted by some of the largest and hottest objects in the visible universe. The necessary data will be provided by a satellite equipped with two sensors: XRISM Resolve and XRISM Xtend. This is the first thing NASA is proud of in its new video:
This “camera” has a specific optical system made of mirrors that creates a radiation funnel, thanks to which it focuses on the aforementioned 36-pixel sensor. Unlike classical photographic matrices, which use the internal photoelectric effect and measure the voltage generated by photons entering the matrix pixels, The solution measures the temperature change of the pixel that absorbs cosmic X-rays. To make this possible, The sensor is cooled using liquid helium to a temperature of 0.05 Kwhich is slightly above absolute zero and below the average temperature of the universe.
Thanks to this information, researchers can learn a lot about the chemical composition of the observed object, among other things, and whether it is moving away from us or approaching us. The XRISM satellite was launched from Japan on September 6, 2023 and is currently providing preliminary data. Correct observation of supernovae, black holes, nebulae, neutron stars, galaxy clusters and other objects It is scheduled to start in July this year. XRISM is unlikely to provide us with images as impressive as the Hubble or James Webb telescopes, but its 36 pixels will allow us to better understand things that these two space telescopes can't even see, and in fact they account for most of the galaxy's mass. The visible universe.
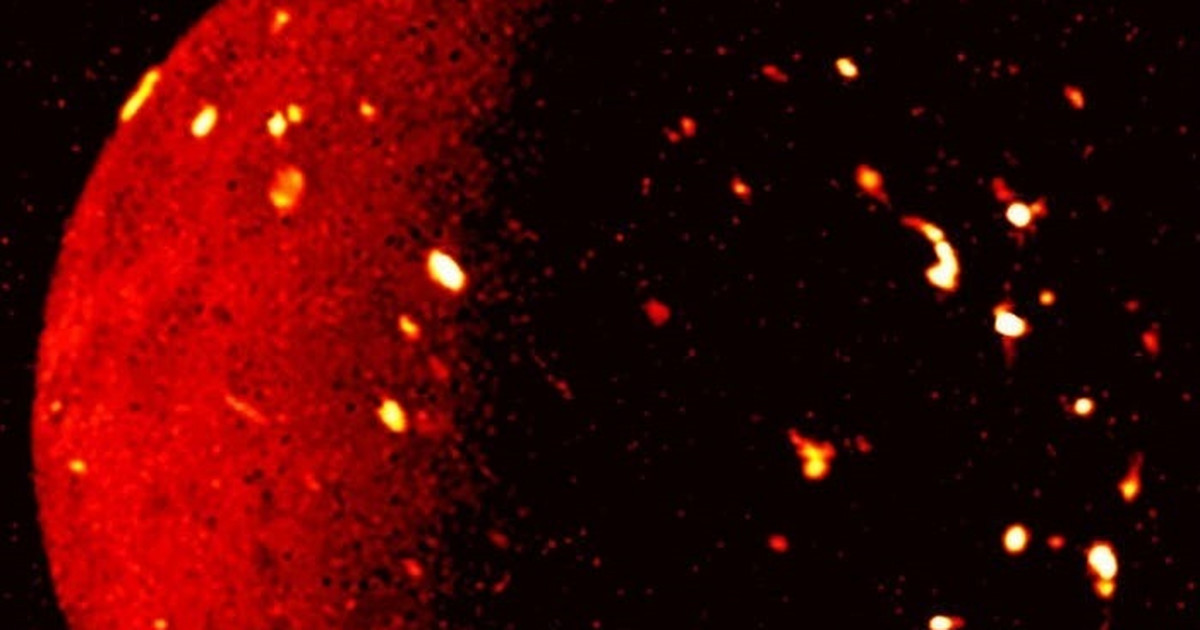
The X-ray spectrum of supernova N132D was obtained using an XRISM Resolve sensor
Are you interested in astronomy and love looking at the sky? Check out the special offer of popular telescopes from our partner offer:

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.