According to the Caltech scientists who developed the solution, it should be particularly useful for studying tissues and biomolecules. This, in turn, should translate into broader possibilities for detecting disease cases or assessing the progression of different types of disease.
Read also: One step is enough to completely change the properties of a substance. Magic straight from the Quantum Realm
The method, known as QMC (Quantum microscope by chance) in more detail in Nature Communications. Among the biggest advantages of this approach, the researchers cite increased speed, improved contrast-to-noise ratio, greater immunity to stray light, higher resolution, and lower intensity illumination.
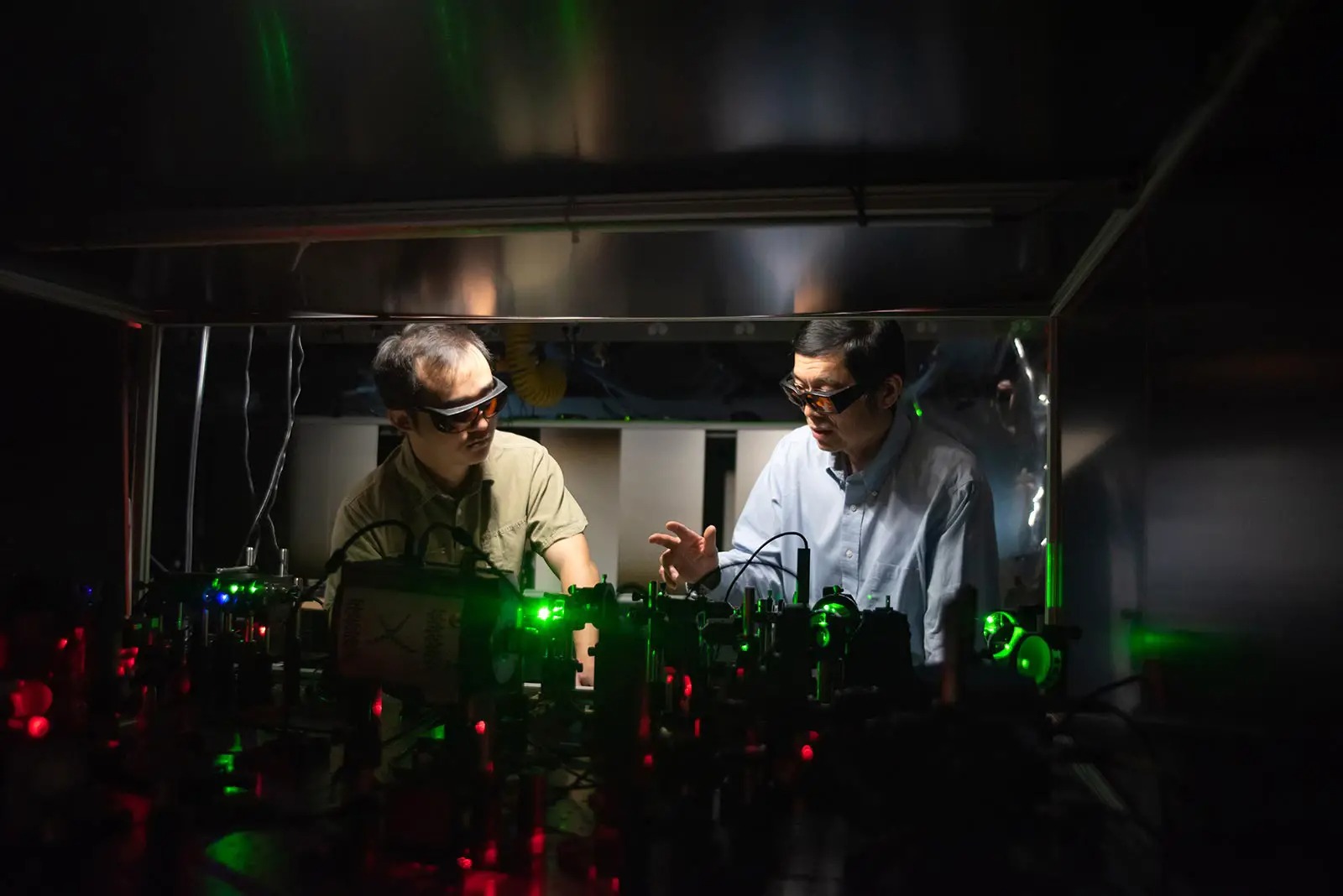
Microscopy is made more efficient by harnessing the benefits of a phenomenon called quantum entanglement
The team members exploited entangled photons by using a type of crystal made of beta barium borate. The laser light transmitted through the crystal was partially converted into two photons, which were then separated using a grid of mirrors, lenses and prisms. One photon was then passed through the tested material, and the second was analyzed, which was possible thanks to the already mentioned quantum entanglement.
Importantly, the microscope can only image features of an object whose minimum size is half the wavelength of light used by the microscope. Reducing the wavelength makes it possible to see smaller structures, which increases the accuracy of the observations.
Read also: Unprecedented quantum entanglement. These numbers speak of fantasy
And while the Caltech team isn’t the first to work on this kind of imaging, it deserves the comfort of a precedence for creating a system that uses such relationships in the real world. In other words, the theoretical assumptions were put into practice and gave the desired results. Additional efforts in this area could increase the number of photons susceptible to entanglement, although each additional photon, unfortunately, reduces the chances of successful entanglement. And this is already very low, about one in a million. These problems stem from the fact that synapses can be disturbed through interaction with the environment

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.