According to the search, the results will be displayed on the pages Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical SocietyUntil the end of the so-called cosmic dawn came about 200 million years later than scientists had previously believed.
The research was based on light from 67 very distant quasars, that is, the combined sources of electromagnetic radiation. According to scientists, the cosmic dawn ended 1.1 billion years after the Big Bang.
Read also: The universe is expanding, but will it always be like this? New study suggests changes
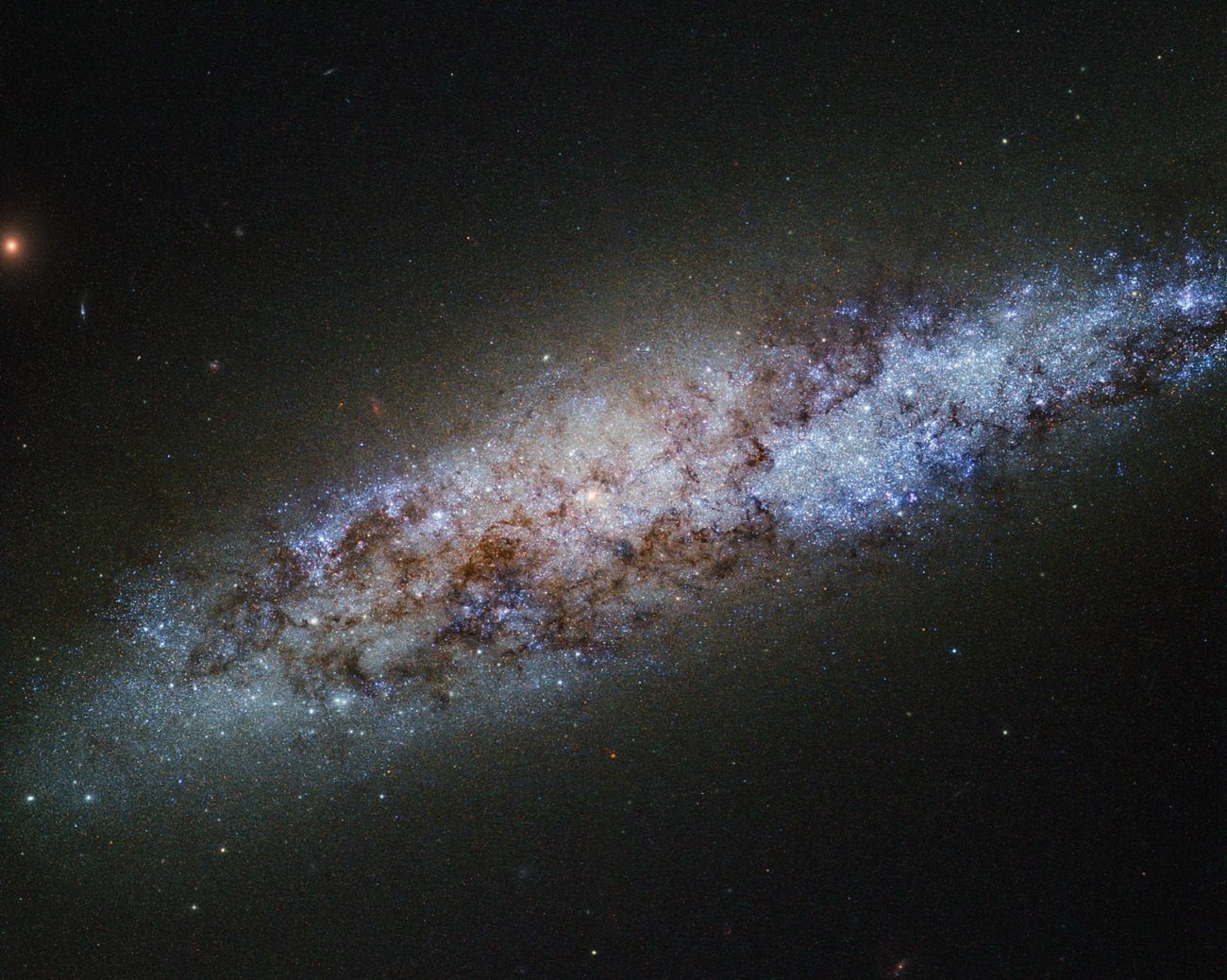
What was this period anyway? In short, this is the time when the first stars began to form. For about 100 million years, beginning about 380,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe was an unusually dark place. It is literally. But at some point, stars and galaxies began to form. The light emitted by them was related to the continuous ionization of intergalactic hydrogen deposits. This process ended when all the hydrogen was ionized, about 1.1 billion years after the Big Bang.
The cosmic dawn is the period associated with the formation of the first stars
The dating team at the time, led by Sarah Bosmann of the Max Planck Astronomical Institute, used optical data from 67 quasars. These objects have been observed with the Very Large Telescope and the Keck Observatory. Powered by supermassive black holes, quasars are far enough away that they formed about a billion years after the Big Bang. The different wavelengths of light emitted, while traveling toward Earth, were absorbed by neutral or ionized hydrogen.
Scientists have also taken into account the fact that the universe is expanding. By analyzing the absorption lines in the spectra of light, the scientists were able to determine when the passage through neutral hydrogen stopped and began to find ionized hydrogen. In the end, they concluded that their estimates so far were inaccurate and off track by about 200 million years. The new date refers to a point in time about 1.1 billion years after the Big Bang.
So we can assume that the first generation of stars and galaxies that drove the reionization is likely to be closer to our planet. In theory, this should make it easier to observe these things, which in turn would translate to being easier to spot in the situation. We still have many secrets, but this type of research allows us to solve at least some of them.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.