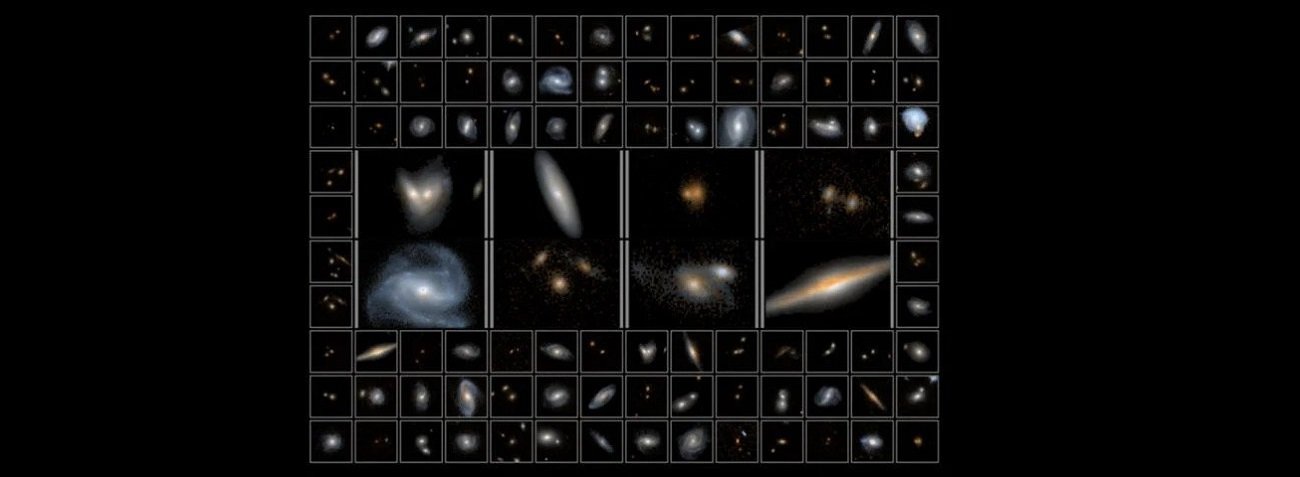
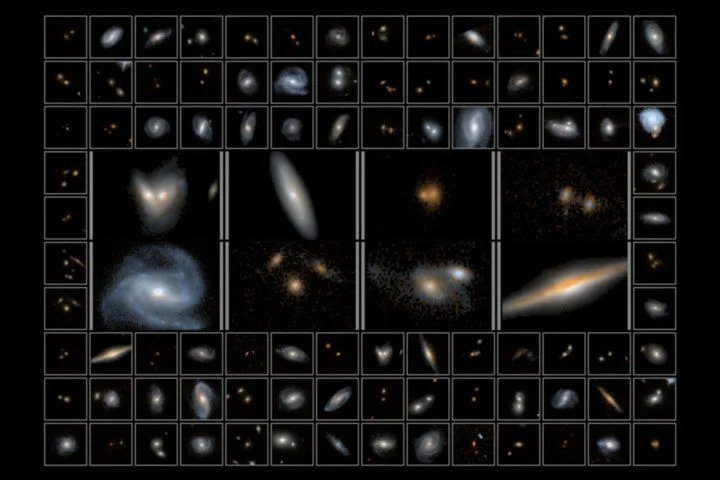
As part of a sky survey called 3D-DASH, astronomers set out to find extremely rare galaxies and other objects that will soon be examined by the James Webb Space Telescope.
His first science observations should take place this month, and the entire mission would take up to several dozen years. During this time, scientists intend to find out both the outermost regions of the universe and find out if life can exist on the selected exoplanets.
Read also: The James Webb Space Telescope cost $10 billion. The new picture shows it’s worth the money
Their successes so far – related to the performance of near-infrared imaging – will be described in the pages Astrophysical Journal. For the first time, they demonstrated that 3D-DASH provides a complete overview of the entire COSMOS domain, one of the richest data fields for extragalactic search beyond the Milky Way. In the near infrared, astronomers are better able to spot early galaxies that recorded record distances from Earth.
Despite its age, the Hubble Space Telescope still has a lot to offer
So far, observations have been limited, but the 3D-DASH technology should help identify rare phenomena such as the activity of black holes, the most massive galaxies in the entire universe, or the merging of such structures. A method known as Drift And Shift (DASH) proved to be the key to these comprehensive and detailed observations from Hubble. It creates an image eight times larger than the standard field of view for this telescope. Many photos are taken and combined into a mosaic.
DASH also produces more images than standard technologies. Instead of one, eight are performed per hour. As a result, in 250 hours of shooting it is what it is before 2000 hours. 3D-DASH covers a total area approximately six times the size of the Moon in the sky as seen from Earth. This record will likely not be broken by even the most advanced James Webb Space Telescope, which is designed for close-up sensitive images and aims to observe small areas in detail.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.