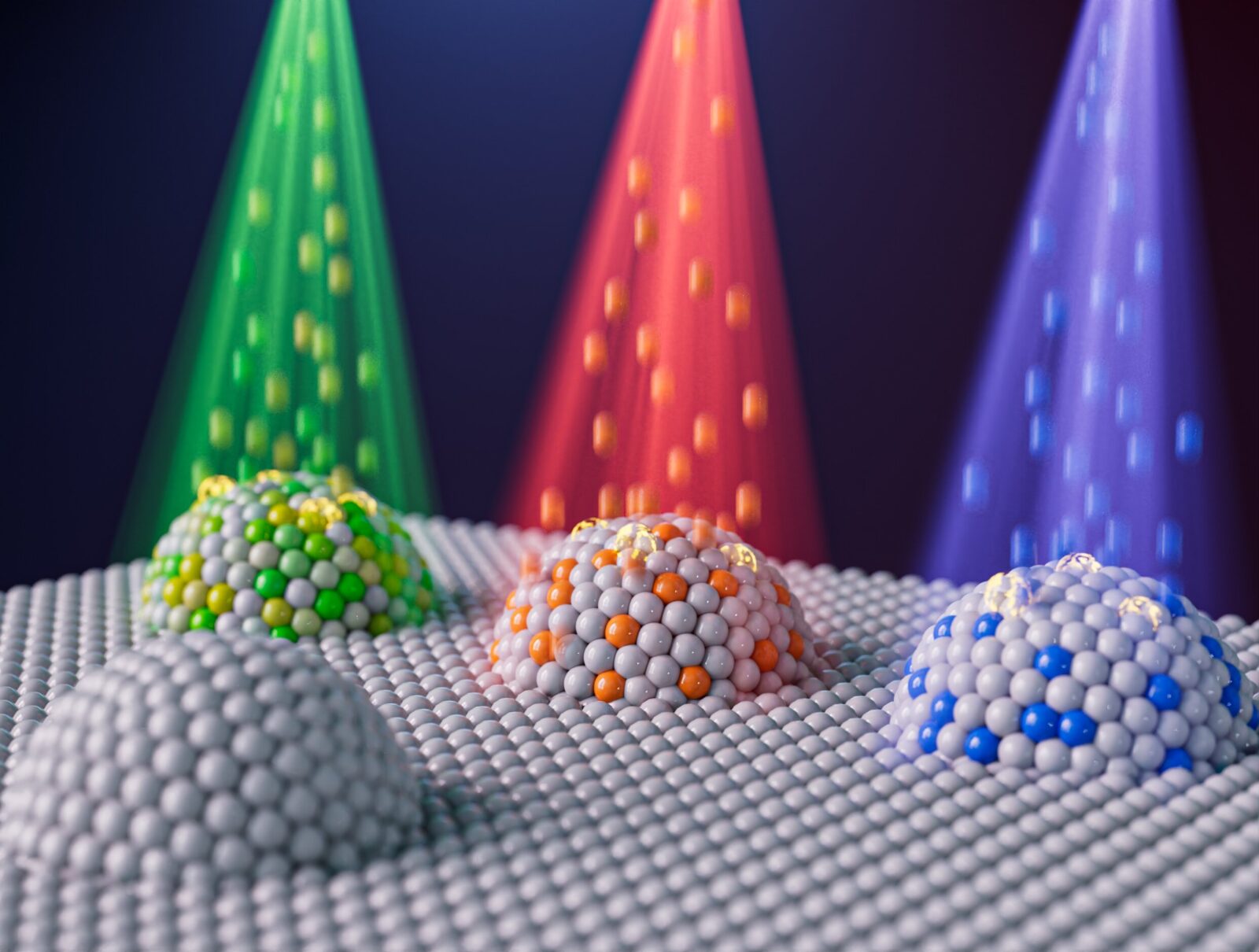
The authors of the experiments conducted in this regard used the ion irradiation method, thanks to which they were able to control the size, composition and various properties of the resulting nanoparticles. We can read about the details of this research in the publication published here Energy and environmental sciences.
Read also: A quantum dot like no other. The machine has accomplished in a few hours what would take a human being many years
As Bilgi Yildiz, who led the effort, explains, the progress has led to significant advances in areas including the design of fuel cells used to generate electricity and the production of hydrogen raw materials that will later be used in the chemical industry.
Fuel cells and electrolysis cells use electrochemical reactions that occur at the cathode and anode electrically separated. The reactions that occur in both parts go in the opposite direction. Catalysts that make reactions occur faster have so far been produced, for example, from metal oxide materials. Unfortunately, they have low durability, and even if such complications could be avoided, there is no way to control the properties of nanoparticles.
Nanoparticles created using ion irradiation can be controlled in terms of their properties
The aforementioned ion irradiation was the key to success. In the course of the experiments, its authors noted that directing an ion beam towards the electrode at the moment when metal nanoparticles dissolved on the surface of the electrode made it possible to control many of the properties of the resulting nanoparticles. What aspects are we talking about? Scientists list the size, composition, density, and location of these nanoparticles.
As an example, members of the research team cite a situation in which irradiation with specific elements led to a change in the structure of nanoparticles. They even managed to resize them and make them much smaller than those created using traditional methods. Yildiz adds that the method used in the experiments, i.e. irradiation, makes it possible to choose which oxide and ion will be irradiated and dissolved.
Read also: There’s nothing there, but there’s still something there. What really is a vacuum?
This leads to many useful possibilities, and as if that were not enough, defects have also been observed in the electrode itself, which could ensure, for example, an increase in the density of the resulting nanoparticles. Moreover, those formed using ion irradiation had a higher catalytic activity than that measured in the case of those formed using conventional thermal melting.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.