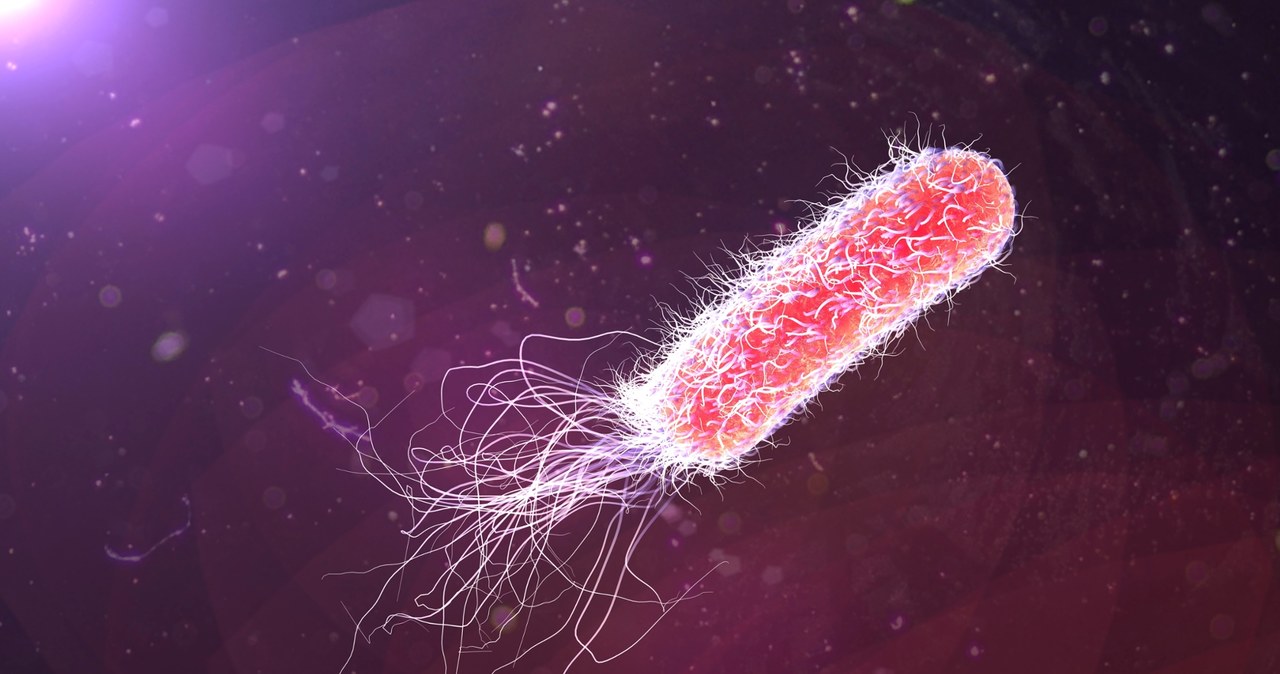
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa It is a Gram-negative bacterium that usually lives in soil and water. Experts say it is one of the most dangerous microorganisms that cause infections in hospitals. Unfortunately, the infection is very difficult to treat due to the high resistance of this pathogen to antibiotics. This bacterium has also topped the World Health Organization’s list of priority pathogens for research and development of new antibiotics.
This pathogen’s adaptability is extraordinary, and it can even survive in jet fuel. This is a big problem, especially for hospitals, where the bacteria are documented in… Most sterile rooms.
Every year, more than 500,000 people worldwide die from P. aeruginosa. These bacteria are usually only dangerous to people with weakened immune systems. However, pathogens can exploit almost any vulnerability in our bodies. immune systemIt was this unique feature that led scientists to wonder what might be behind this mystery.
Based on 596 closely related bacterial strains collected from over 9,800 sources worldwide (some dating back to 1900!) The genetic family tree of the pathogen was developed..
The research showed that only 21 strains are responsible for the vast majority of infections. The researchers point out that The unique virulence of bacteria has evolved over the past two centuries..
It was also noted that several strains had developed a strong affinity for people with cystic fibrosis. Analyses showed that These strains have developed targeted ways to enter the bodies of people with cystic fibrosis, bypassing the immune system.Meanwhile, the microorganisms accumulated in the same immune cells that were supposed to destroy the pathogens. Then the bacteria evolved and began to exchange information about resistance just like… cooking recipes.
The new discoveries clearly demonstrate the pathogen’s amazing ability to exploit its own capabilities, the scientists said. Adaptability To live in new niches in harsh environments. This ability gives these bacteria space to accumulate and create new ways to expand and grow. Another evolutionary leap.
Now there is greater pressure to develop new screening mechanisms and isolation methods. Experts agree that gathering knowledge about the pathogen’s strengths is essential to finding an effective way to stop it.
The research results were published in a prestigious international scientific journal. Sciences.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.