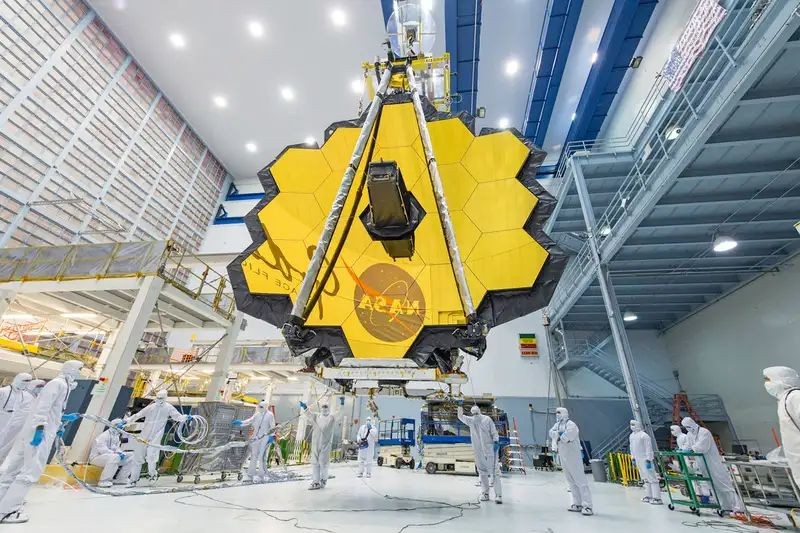
The Webb Telescope (JWST) is already located more than 1.3 million kilometers from Earth and has put its primary and secondary mirrors in the starting position for several days. This process will take a few more days because the individual parts of the main mirror They move at a grass growth rate of about 1 mm per day. Meanwhile, the telescope reaches its target less than 130 thousand km – spill point L2. The highest temperature on the hot side of JWST is 56°C, and the lowest on the cold side has already fallen to -206°.


At the time of launch, individual parts of the mirror were secured from behind with three metal pins. Now they have to free themselves from these pegs in order for them to move, which will allow them to center to act as one big mirror. Each part should move 12.5 mm.
It takes a lot of patience to perform this process. The actuators that drive the parts are designed to make extremely precise and small movements. As a result, each part can be tuned to a precision of 10 nanometers (about 1/10000 the thickness of a human hair). However, this design of the actuators means that when much larger movements have to be done, a lot of time is required. Moreover, the mirror control system can only move one actuator at a time. This architecture was chosen because it is simpler from the point of view of the complexity of the electronics controlling the whole and more secure, since computers and sensors can focus on monitoring a single actuator that is currently in operation. Moreover, in order to reduce the amount of heat that reaches the mirror from the actuators, each actuator can only be moved for a short time. Therefore, it takes a long time to move each 12.5 mm part.
Once all parts are released from their warranties, the process of precisely aligning the parts to function as a single mirror will begin over a period of several months.
In the attached drawing, you can see what phase the primary mirror and secondary mirror (SM) sectors were at the time this information was written. The main mirror is divided into three sections with different optical properties. Each section consists of six sections. As we can see, most of them are already raised by 7.5 mm and are under the final position by 5 mm. Only the A3 and A6 pieces have not moved yet. They will be lifted separately at the end of the process as their position sensors operate differently than others.

Echo Richards embodies a personality that is a delightful contradiction: a humble musicaholic who never brags about her expansive knowledge of both classic and contemporary tunes. Infuriatingly modest, one would never know from a mere conversation how deeply entrenched she is in the world of music. This passion seamlessly translates into her problem-solving skills, with Echo often drawing inspiration from melodies and rhythms. A voracious reader, she dives deep into literature, using stories to influence her own hardcore writing. Her spirited advocacy for alcohol isn’t about mere indulgence, but about celebrating life’s poignant moments.